Attitude of intending couple toward compulsory HIV screening test: A means to control the spread of HIV infection
- Corresponding Author:
- M. A. Momoh
Department of Pharmaceutics, University of Nigeria Nsukka, Enugu State
E-mail: jointmomoh@yahoo.com
Date of Received: 04-04-2010
Date of Modified: 19-04-2010
Date of Accepted: 02-05-2010
Available Online: 15-05-2010
Abstract
The objective of questionnaire based survey was to assess the attitude and acceptability toward compulsory HIV screening for the intending couple. A structure questionnaire was used to elicit responses from the couples. Data were collected from total 1150 volunteers, that was disaggregate by sex but education and social status were not put in to consideration during the study. Higher percentage of awareness and knowl-edge were found about modes of transmission, high risk factors, self protection, response were favourable with female than male in vertical transmission or through breast milk. Despite of not knowing the HIV status, 25-48% population willingly agreed to undergo test but larger population disagreed. This finding definitely seems that a lot need is there to enhance the acceptability of the testing, the long distance driver more education on the prevalent of the pandemic, legal intervention will also help.
Keywords
compulsory, couple, HIV, screening
Introduction
There is no obvious figure or statistics to evaluate the number of people living with HIV infection in Nigeria. Several studies have identified a big gap in adequate data management as it concerned Nigeria health system. According to National Agency for the Control of Aids (NACA), HIV/AIDS is said to mainly affecting people in the productive classes and living much burden on the aged parent to take care of the very little young generation that have been come an orphan due to HIV/AIDS pandemics [1]. The majority of the age group that are vulnerable to this malicious infection are within the age of (15-45 years, these age groups were considered as the working force of any viable nations [2]. Researches have shown that, if the case is not properly checked, the number will be double in the year 2020 (3). Study have shown that several factors involved in the spreading of this infection includes: sharing an infected sharp objects, contaminated biological fluids, infected intravenous drugs users, transmission from mother to child (through birth and breast feeding), unprotected sexual relationship with an infected person and blood transfusion have been identified. The worst of these offenders has been through sexual transmission [3]. The global negative effects of HIV/AIDS pandemics have been felts in all area of life, theses includes: health, education, agriculture, food security, social and economic infrastructures are worst causalities. At present, there is no cure and most activities are aimed at reducing HIV transmission, voluntary counselling and testing is one of the strategies employed in the effort to control the global HIV/ AIDS pandemic [4]. Voluntary counselling and testing has been found to be effective in changing high risk behaviours and more than 40% reduction in unprotected intercourse among individuals who received, compared to those who received voluntary counselling and testing (VCT) health information only has been reported [4]. Unfortunately, the majority of Nigerians do not know their status and this proportion is highest in countries worst affected by the epidemic [5]. HIV/AIDS prevention and control strategies in addition to the encouragement of behavioural modification and provision of antiretroviral drugs are essential ingredients in the fight against HIV/AIDS. Strategies that are most appropriate are the early detection of the various, reduction in casual sex, proper blood screening and prevention of mother to child transmission are much desire in pregnant women. Generally, information on preventive controls highlighted routinely by government agencies and voluntary organization in media and dailies about the use of condomsdisposable syringe, do not use paid blood donor and faithful to the partner. Prevention by effective vaccination is still remains a dream. Prediction of increasing number of HIV cases may be due to illiteracy, improper knowledge and awareness about AIDS. To curb this, coordinated efforts from all disciplines of the health care system and some amount of legislative interference is needed against the disease [6]. More importantly religion have a lot to do in this case, several religious leader both in the mosque and churches have take the front seats in the strive to cub this ailment, part of the strategies is the mandatory blood screening that is been utilised by the catholic faithful to help in early detection of infected person and to reduce the rate of spread. Many of the faith see the measure as unethical while some see it as a means to help protect their fellow human being. Because of these different view points on the subject matter, this study aims at evaluating the willingness for compulsory HIV/AIDS testing among the intending couples, a hospital-based study
Study Area
The study was done in Bishop Shanahan hospital centre, the one of the approved centre for HIVscreening centre in Nsukka area, this centre was also the only accredited centre for the Roman Catholic denomination Christian approved for pre-marital screening test. The hospital ranks the first in the zone, now the centre is a referral centre for the HIV/AIDS treatment and other medical cases in the zone.
Study Population
Inclusion Criteria
All clients that came for a pre-marital test within the study period and agreed to took part in the study were included in the study
Exclusion criteria
Clients that have not come for full pre-marital test and those that came but declined from taken part in the study were excluded from the sample study.
Sampling
Random sampling was used in the study with a total of 1150 clients that came for routine pre-marital test which comprises of blood group, genotype and HIV screening in our health centre. Data were collected using a semi-structured and self administered questionnaire.
Analysis of Data
Data were analyzed by Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS) and for multiple, comparism ANOVA was used.
Ethical Issue
All the clients involved in the study were requested to give their consent willingly, without any form of compulsion, verbal consent was considered as sign of agreement. Information obtained were treated confidentially, clients name and address were completely avoided.
Results And Discussion
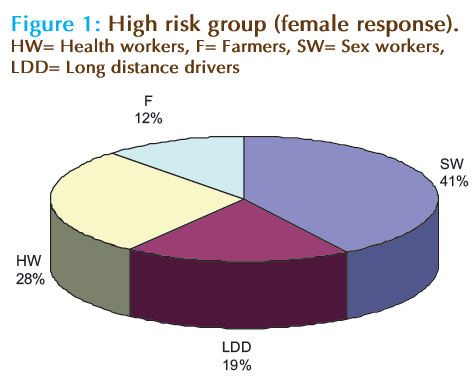
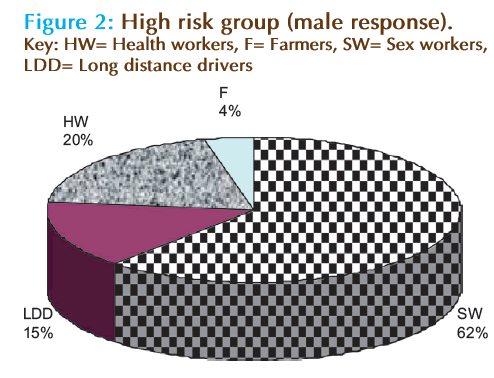
A finding on the risk factor shows that all the clients have the knowledge on the possible risk behaviours. In the present study, majority of the respondent agreed that sexual worker were more prone to the infection than any other profession (Fig. 1). A total of 42% of the female agreed on the sex workers while 62% male supported, this implied that male are more sensitive to the risk associated with sex workers than female, this could be the possible reason while the trade is still thriving high because female never believed that they are on high risk trade. The difference in there response is statistical significant at P > 0.005. On the other hand, long distance driver (LDD) has been third major group that are vulnerable to this infection. It has been researched that majority of the drivers have more than one sexual partner and in most cases they had relationship without using condom [7]. This explained the role of drivers in the spread of HIV [8]. In the response here for male (15%) and female (19%), the response of female tally with response from oral interview from the wives of long distance drivers on the sexual behaviour of their husband when they returned home, in the oral interviewed they all agreed that, their husband show negative attitude toward them whenever they approach their husband for sexual relation, which indirectly indicated that they have other sex partners as they ply their trade (Fig. 1 and 2).
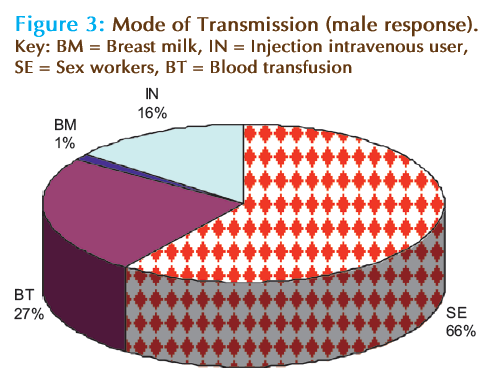
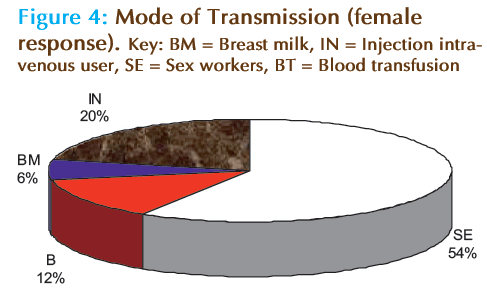
Figures 3 and 4, depicted knowledge on the means of transmission through a sexual route, sharing needles containing infected blood, transfusion of infected blood, transmission through an infected mother to foetus among overall male and female population. Pie chart representation clearly suggested that 54% female were of the opinion that sexual route was the highest compared to 20% who agreed on injection using HIV contaminated needle, this was followed by 12% in blood transfusion and least 6% through breast milk of an infected mother. The result tally with response from the male counterpart but the figure varies. A total of 66% settled for sex as the major route of transmission. The results were in agreement with various research that believed that the major routes of transmission is through sexual intercourse with an infected person, all the respondent show an average knowledge on the mode of transmission despite their education background. We have previously published a study on the sexual transmission route and that effort can be channelled through early detection [9]. Majority of the male never believed that HIV can be transmitted through breast milk or vertical transmission, very interesting and valuable findings that females were more aware about transmission through an infected mother to her unborn baby as compared to male [10].
Majority of the population rejected the idea of making testing of HIV compulsory, only a few number agreed on making it compulsory and the majority in this are female. Oral interviewed show that large number rejected it based on the financial involvement while few based their reason on social aspect, if eventually one becomes positive. In response to the question, both sex agreed on the important of the screening as a means of halting the spread, still the response are more positive on the female than the male, although the variation was not statistically (SPSS version 6) signifi- cant (Table. 1). The entire participant except few agreed that HIV is real and no respecter of age or race [9]. This study is in agreement with our earlier publication on the same subject where we assessed the level of seropositive among the intending couple [10].
| Question Sex | Responses in % | |
|---|---|---|
| Yes | No | |
| Is it good making HIV test compulsory? | ||
| Female: | 36 | 64 |
| Male. | 23 | 77 |
| Can compulsory screening halt the spread? | ||
| Female: | 54 | 46 |
| Male. | 43 | 57 |
| Do you agree that HIV is real? | ||
| Female: | 74 | 26 |
| Male. | 65 | 35 |
Table 1: Response to the structure questions
Conclusion
This finding definitely seems that pre-marital test is among the criteria to fight the spread of this pandemic disease that has come to wipe out human race.
References
- Anonymous. A million more with HIV, In: Africa health. 2000; 23: 11-17
- Onoja AJ, Shehu MB, Abu A, et al. A Baseline HIV-1 prevalence among various risk group in Nigeria: International AIDS conference Bangkok Book of abstract 2004;116.
- Laurice GE, “Grim Report on AIDS Epidemic Newsray: International conference on AIDS, Bacelona. 2002; 178-197.
- Merson MH. The HIV-AIDS pandemic at 25 – the global response. N. Engl. J. Medicie. 2006; 354:2414-2417.8
- National HIV sero-prevelence sentinel Survey. Federal Ministry of Health, National AIDS/STD Control program. April 2004, Abuja Nigeria
- Malavade JAB, Shah SR, Shah JJ, et al. Ethical and legal issues in HIV/AIDS counseling and testing, the XIV International AIDS Conference, 2002; 231-239
- Centers for Disease Control (2001). The global epidemiology of HIV/ AIDS. Br. Med. Bull. 58:7-18.
- Reeves JD, Doms RW. Human immunodeficiency virus type 2. J. Gen. Virology. 2002; 83: 1253-1265.
- Ghosh TK. AIDS: a serious challenge to public health, Journal of the Indian Medical Association. 1986; 84:29.
- UNICEF, Press release. Reducing mother-to-child transmission of HIV/AIDS in India, 2005; 132-144
- Peter E, Badcock W. Managing the Impact of HIV/AIDS in Education in Kwazulu Natal: A presentation to the National Teachers Union Advocacy Conference on HIV/AIDS. 2002.
- Momoh, M. A , Ezugworie, O. J. and Okonta J.M. Prevalence of HIV- 1 and 2 seropositivity among intending couples screened in peri-urban hospital in Nsukka zone, Enugu state, Nigeria. Journal of pharmaceutical and Allied science. 2009; 2: 755-760.